European Patent Convention (EPC)
|
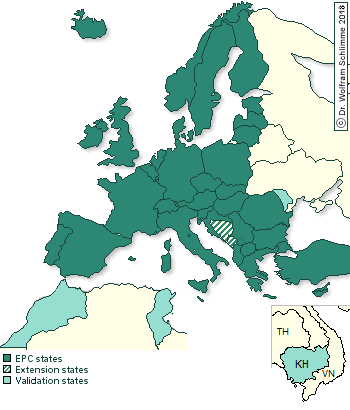
A European Patent may be applied for the below mentioned states: Albania, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Switzerland and Liechtenstein, Croatia, Czech Republic, Germany, Denmark, Estonia, Spain, Finland, France, United Kingdom, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Macedonia (former Yugoslav Republic), Malta, Monaco, The Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, San Marino, Serbia, Sweden, Slovakia, Slovenia, Turkey, Cyprus. Granted European Patents may be extended to: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro Granted European Patents may also be validated in: Morocco, in the Republic of Moldova, in Tunisia and in Cambodia.
If the United Kingdom is designated in a European Patent the patent protection can also be extended to Hong Kong.
For information about the national validation of a European Patent, please click
|
 |
||
| Compare EPC and EU countries. |
[ close window ]